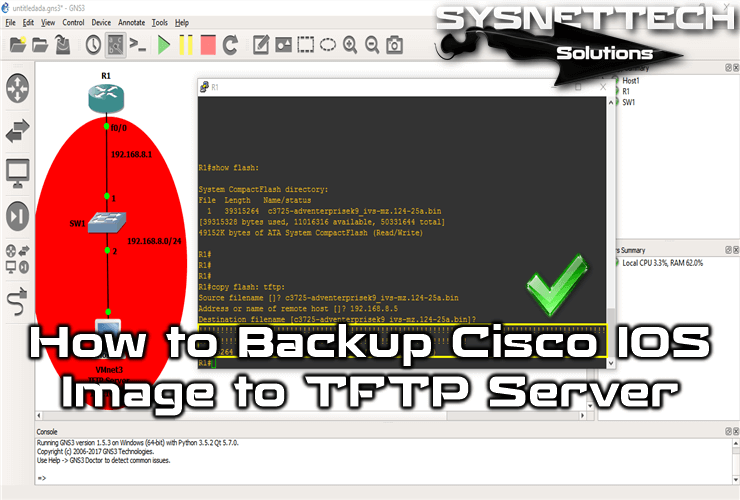
- Cisco Copy Tftp Command
- Cisco Asa Tftp Server Command
- Configure Tftp Server Cisco
- Cisco Tftp Server Commands Bot
- Cisco Switch Tftp Server
- Cisco Tftp Server Software
- Cisco Router Tftp Server Commands
IOS includes a built-in FTP client that can be used to transfer images to and from the Cisco device. Unlike TFTP, FTP supports authentication, and you will need to provide a valid FTP server username and password.
Cisco Copy Tftp Command
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) – TFTP is a simple file transfer protocol which is either used to put or get a file from a remote host. It uses UDP port number 69. But TFTP is used where no authentication and control is required. The snmp-server tftp-server-list command is still supported in Cisco IOS software, but if it is configured as snmp-server tftp-server-list 10, it will be substituted with the snmp-server file-transfer access-group 10 protocol tftp command.

The following steps are required for FTP transfers:
- create an FTP username and password by using the ip ftp username USERNAME and ip ftp password PASSWORD global configuration command. We need to provide the username and password that were already created on the FTP server.
- issue the copy ftp flash exec mode command and follow the wizard.
Here is an example. Let’s say that we want to transfer the image file from the FTP server to a Cisco switch. We can do this using the following set of commands:
To verify that the file has indeed been transfered, we can use the show flash: command:
We can also transfer files from the IOS device to the FTP server, for example to backup the startup configuration. Here is an example of copying the startup configuration of a switch to the FTP server:
Home > Articles > Cisco
 ␡
␡Cisco Asa Tftp Server Command
- Installing Cisco IP Phone Firmware and XML Configuration Files
This chapter is from the book
This chapter is from the book
Installing Cisco IP Phone Firmware and XML Configuration Files
Certain files are necessary for the proper operation of a Cisco IP phone or analog device so that it can register successfully with a Cisco Unified Communications call control device. These files are not installed on the Cisco router and must be installed from an external source. The file types are as follows:
- Firmware: The firmware is loaded into flash memory on the IP phone and can survive a reboot.
- SEPAAAABBBBCCCC.cnf.xml: This XML configuration file is specific to one device, and the AAAABBBBCCCC part of the name is the MAC address of the device.
- XMLDefault.cnf.xml: This XML configuration file specifies the proper firmware and the call agent's address and port, which the new phone needs to register.
The following sections describe each file type in greater detail.
Firmware
Install the firmware required by the Cisco IP phones in the flash memory of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express systems. There are two commands required to provide access to these firmware files:
- tftp-server flash:firmware-file-name: Use this global command to make the file available.
- loadphone-type firmware-file: Use this telephony-service command to associate a type of phone with a firmware file.
All the necessary firmware files for Cisco IP phones are stored internally in the flash memory of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express router, so an external database or file server is not required. During registration, Cisco IP phones use TFTP to download firmware files from the router's flash memory. All Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express configuration and language files are located in the memory of the router in the system:/its/ directory.
To make the firmware file(s) available through a TFTP server, use the tftp-server flash:firmware-file-name(s) command on the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express router. The loadphone-type firmware-file command under telephony service is also required to associate the model of IP phone with the appropriate firmware file(s).
For Cisco Unified Communications Manager, the firmware files are installed on the server(s) in the cluster that run the TFTP service.

Device Configuration XML File
The XML file SEPAAAABBBBCCCC.cnf.xml (where AAAABBBBCCCC is the MAC address of the IP phone) contains the call agent IP address and port, firmware, locale, directory URL, and many other pieces of information. This file is present when the IP phone has been added to the configuration.
Listing 7.8 shows a configuration file that contains the phone model (7931), IP address (10.6.150.1), and port (2000) for registering; the firmware filename; the language (English United States); and additional information for proper IP phone operation. Microsoft office toolkit 2010 download.
Listing 7.8. SEPAAAABBBBCCCC.cnf.xml File (AAAABBBBCCCC = the MAC Address)
Default XML File
IP phones and devices that do not find the more specific SEPAAAABBBBCCCC.cnf.xml file can use the XMLDefault.cnf.xml file if they have never registered before and an autoregistration method has been enabled. IP phones that download this XML file through TFTP learn the IP address and port to send Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) messages to when attempting to register. The IP phones also learn the version of firmware that is required to function properly with the Cisco Unified Communications call control product to which the phone is registering. Sims castaway pc download. Cisco IP phone models 7931 and 7961 are highlighted.
Configure Tftp Server Cisco
Listing 7.9 shows a default configuration file. Typhoon rising download.
Cisco Tftp Server Commands Bot

Cisco Switch Tftp Server
Listing 7.9. XMLDefault.cnf.xml File
Related Resources
Cisco Tftp Server Software
- Book $63.99
Cisco Router Tftp Server Commands
- Book $39.99
- Premium Edition eBook $39.99
